Processors used in Dell computers
The following processors are currently used in Dell tablets, laptops and desktop models.
Intel Tablet Processors
One Intel Atom Z2760 (1.5+GHz, 512kB x2 cache, Dual Core)
Intel Laptop Processors
Celeron
Intel® Celeron® B815 processor (1.60GHz,1333,2M cache)
Intel® Celeron dual core B820 (1,7 GHz)
Pentium
Intel Pentium B960 (2,20GHz,2M cache, dual core)
Intel Pentium Dual Core P6200 (2.13GHz)
Core i3
Intel® Core™ i3-2350M (2,30 Ghz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i3-2328M (3 Mo Cache, 2.2 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-2330M (2.20 GHz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i3 2357 (1,3 GHz, 3 M cache)
Intel® Core™ I3-380M (2,53 GHz)
Intel Core i3-2370M (3 Mo Cache, 2.40 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-2367M (1.4GHz with Intel HD Graphic 3000 (WWAN)
Intel Core i3-3217U (1.8GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-3110M (2,40 GHz, 3 Mo)
Core i5
Intel® Core™ i5-2430M (2.40 GHz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i5-2450M (2,50 GHz with Turbo Boost to 3,10 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5 2467M 1.6GHz (3MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ I5-2520M (2.50GHz, 3 MB cache, Dual Core)
Intel® Core™ i5-3210M (3M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
Intel®Core™ i5-3317U 1.7GHz with 1GB AMD Radeon HD7570M (WWAN)
Core i7
Intel® Core™ i7-2670QM processor 2.20 GHz with Turbo Boost up to 3.10 GHz
Intel® Core™ i7 Processor 2760QM (2.40Ghz, 6MB, 4C)
Intel® Core™ i7 2617M 1.5GHz (2.6GHz w/Turbo Boost, 4MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ i7 2630QM (2 GHz, 8 threads, 6M cache)
Intel® Core™ i7 2637M 1,7 GHz (2,8 GHz with Turbo Boost, 4 M cache)
Intel® Core™ i7-2640M processor 2.80 GHz with Turbo Boost 2.0 up to 3.50 GHz
Intel® Core i7-2760QM (2,40 GHz, 6 MB cache, Quad Core)
Intel® Core I7-2860QM (2.50GHz, 8MB cache, Quad Core)
Intel® Core™ i7 2960XM Overclocked Turbo Boost (8MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ i7-3610QM (6MB Cache, up to 3.3GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3612QM processor (6M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i7-3720QM (6MB Cache, up to 3.6GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3517U processor 1.90 GHz with Turbo Boost 2.0 up to 3.00 GHz (UMA Graphics & TPM Inc
Intel® Core™ i7 3920XM (8MB Cache, up to 3.8GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3632QM (2.2GHz)
Intel Desktop processors
Celeron
Intel® Celeron® G645 (1,90 GHz, 1.5 Mo)
Pentium
Intel® Pentium® G620 (2,60GHz, 3Mo)
Intel® Pentium® G630 (2.70GHZ, 3MB)
Core i3
Intel® Core™ i3-2120 (3,30GHz, 3Mo)
Intel® Core™ i3-3220 (3.3 GHz, 6 Mo)
Intel® Core™ i3-3225 (Dual Core, 3.30GHz, 3MB)
Core i5
Intel® Core™ i5-2310 (2.90GHz, 6MB)
Intel® Core™ i5-2320 (3 GHz, 6 Mo)
Intel® Core™ i5 2400 (3.10GHz, 6Mo)
Intel® Core™ i5-3450S (6M Cache, 2.80 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5-3350P (6M Cache, up to 3.3 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5-3570S (3,10 GHz, 6 Mo with HD2500 integrated graphics)
Core i7
Intel® Core™ i7-2600 (3.4GHz, 8MB Cache) Quad Core Processor with overclocked Turbo Boost to 3.9GHz
Intel® Core™ i7-3820 (Four Core, 10MB Cache) 3.60GHz
Intel® Core™ i7-3770 (3.40GHz, 8MB) 3rd generation
Intel Tablet Processors
One Intel Atom Z2760 (1.5+GHz, 512kB x2 cache, Dual Core)
Intel Laptop Processors
Celeron
Intel® Celeron® B815 processor (1.60GHz,1333,2M cache)
Intel® Celeron dual core B820 (1,7 GHz)
Pentium
Intel Pentium B960 (2,20GHz,2M cache, dual core)
Intel Pentium Dual Core P6200 (2.13GHz)
Core i3
Intel® Core™ i3-2350M (2,30 Ghz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i3-2328M (3 Mo Cache, 2.2 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-2330M (2.20 GHz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i3 2357 (1,3 GHz, 3 M cache)
Intel® Core™ I3-380M (2,53 GHz)
Intel Core i3-2370M (3 Mo Cache, 2.40 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-2367M (1.4GHz with Intel HD Graphic 3000 (WWAN)
Intel Core i3-3217U (1.8GHz)
Intel® Core™ i3-3110M (2,40 GHz, 3 Mo)
Core i5
Intel® Core™ i5-2430M (2.40 GHz, 3M cache)
Intel® Core™ i5-2450M (2,50 GHz with Turbo Boost to 3,10 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5 2467M 1.6GHz (3MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ I5-2520M (2.50GHz, 3 MB cache, Dual Core)
Intel® Core™ i5-3210M (3M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
Intel®Core™ i5-3317U 1.7GHz with 1GB AMD Radeon HD7570M (WWAN)
Core i7
Intel® Core™ i7-2670QM processor 2.20 GHz with Turbo Boost up to 3.10 GHz
Intel® Core™ i7 Processor 2760QM (2.40Ghz, 6MB, 4C)
Intel® Core™ i7 2617M 1.5GHz (2.6GHz w/Turbo Boost, 4MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ i7 2630QM (2 GHz, 8 threads, 6M cache)
Intel® Core™ i7 2637M 1,7 GHz (2,8 GHz with Turbo Boost, 4 M cache)
Intel® Core™ i7-2640M processor 2.80 GHz with Turbo Boost 2.0 up to 3.50 GHz
Intel® Core i7-2760QM (2,40 GHz, 6 MB cache, Quad Core)
Intel® Core I7-2860QM (2.50GHz, 8MB cache, Quad Core)
Intel® Core™ i7 2960XM Overclocked Turbo Boost (8MB Cache)
Intel® Core™ i7-3610QM (6MB Cache, up to 3.3GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3612QM processor (6M Cache, up to 3.10 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i7-3720QM (6MB Cache, up to 3.6GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3517U processor 1.90 GHz with Turbo Boost 2.0 up to 3.00 GHz (UMA Graphics & TPM Inc
Intel® Core™ i7 3920XM (8MB Cache, up to 3.8GHz w/ Turbo Boost 2.0)
Intel® Core™ i7-3632QM (2.2GHz)
Intel Desktop processors
Celeron
Intel® Celeron® G645 (1,90 GHz, 1.5 Mo)
Pentium
Intel® Pentium® G620 (2,60GHz, 3Mo)
Intel® Pentium® G630 (2.70GHZ, 3MB)
Core i3
Intel® Core™ i3-2120 (3,30GHz, 3Mo)
Intel® Core™ i3-3220 (3.3 GHz, 6 Mo)
Intel® Core™ i3-3225 (Dual Core, 3.30GHz, 3MB)
Core i5
Intel® Core™ i5-2310 (2.90GHz, 6MB)
Intel® Core™ i5-2320 (3 GHz, 6 Mo)
Intel® Core™ i5 2400 (3.10GHz, 6Mo)
Intel® Core™ i5-3450S (6M Cache, 2.80 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5-3350P (6M Cache, up to 3.3 GHz)
Intel® Core™ i5-3570S (3,10 GHz, 6 Mo with HD2500 integrated graphics)
Core i7
Intel® Core™ i7-2600 (3.4GHz, 8MB Cache) Quad Core Processor with overclocked Turbo Boost to 3.9GHz
Intel® Core™ i7-3820 (Four Core, 10MB Cache) 3.60GHz
Intel® Core™ i7-3770 (3.40GHz, 8MB) 3rd generation
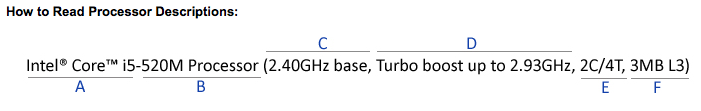
A — This describes the type of processor you are purchasing.
B — This is known as the processor number. In general, the higher the processor number the higher the performance.
C — This is the clock speed or the speed at which the CPU processes information.
D — Turbo boost is a new feature which automatically speeds up your processor when your PC needs extra performance, giving you extra power when you need it and saving battery when you don’t. What you get is performance on demand during peak usage when the processor is operating below maximum capacity. In the example above, the processor with turbo boost feature can increase clock speed from 2.4GHz up to 2.93GHz. Turbo boost technology is available on Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i7 processors only.
E — 2C indicates there are two cores on a single processor, giving you more power to multitask.
4T indicates 4 threads, so you can multitask faster and experience less wait time.
F — This is the amount of L3 cache available to the processor.
B — This is known as the processor number. In general, the higher the processor number the higher the performance.
C — This is the clock speed or the speed at which the CPU processes information.
D — Turbo boost is a new feature which automatically speeds up your processor when your PC needs extra performance, giving you extra power when you need it and saving battery when you don’t. What you get is performance on demand during peak usage when the processor is operating below maximum capacity. In the example above, the processor with turbo boost feature can increase clock speed from 2.4GHz up to 2.93GHz. Turbo boost technology is available on Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i7 processors only.
E — 2C indicates there are two cores on a single processor, giving you more power to multitask.
4T indicates 4 threads, so you can multitask faster and experience less wait time.
F — This is the amount of L3 cache available to the processor.
Understanding processor specifications
There are several elements in the specifications provided by processor manufacturers. The overall performance of a processor is the result of how these specifications combine to facilitate calculation and distribution of data. Here is a short glossary of processor terms to help you understand procesor specifications:
Core --Even if you're not running multithreaded software programs (such as video editors), having multiple processing cores on a single chip improves performance because Windows can run its background tasks on the second core, freeing the first core to run programs of your choice, unimpeded. (You'll notice this most when you are running multiple applications simultaneously.) The increase in power you'll notice with four cores as opposed to two is even more dramatic—assuming you're using apps that support all four cores
FSB (Frontside bus) speed--Measured in MHZ, front-side bus (FSB) speed is the rate at which an Intel processor communicates with the motherboard's memory controller. A high FSB speed boosts the performance of RAM-intensive operations, thus cutting the time it takes for data to move between the CPU and the memory controller. The upper limit of FSB speeds today on Intel's highest-end Core 2 Extreme processors is 1,600MHz, while older processors have FSB speeds of 800MHz, 1,066MHz, or 1,333MHz.
L2 Cache--Cache stores memory data and speeds up operation by making recently accessed data immediately available to the processor. Generally, the larger the L2 cache, the bigger the performance increase you can expect, at least with Intel CPUs that utilize one larger shared cache. Today, cache size runs in the 512 KB to 8 MB range. AMD processors, on the other hand, give each core its own cache.